Featured News

Kavli Prizes are among the most prestigious awards in scientific research. They are presented every two years to scientists who have made transformational discoveries in astrophysics, nanoscience and neuroscience. Kanwisher, the Walter A. Rosenblith Professor of Cognitive Neuroscience and an investigator at the McGovern Institute, is being honored, along with research partners Doris Tsao of the University of California at Berkeley and Winrich Freiwald at the Rockefeller University, "for the discovery of a highly localized and specialized system for representation of faces in human and non-human primate neocortex."
Featured News

Language is a defining feature of humanity, and for centuries, philosophers and scientists have contemplated its true purpose. We use language to share information and exchange ideas—but is it more than that? Do we use language not just to communicate, but to think? McGovern Investivator Ev Fedorenko in the Martinos Imaging Center at MIT. Photo: Caitlin Cunningham In the June 19, 2024, issue of the journal Nature, McGovern Institute neuroscientist Evelina Fedorenko and colleagues argue that we do not. Language, they say, is primarily a tool for communication.
Featured News
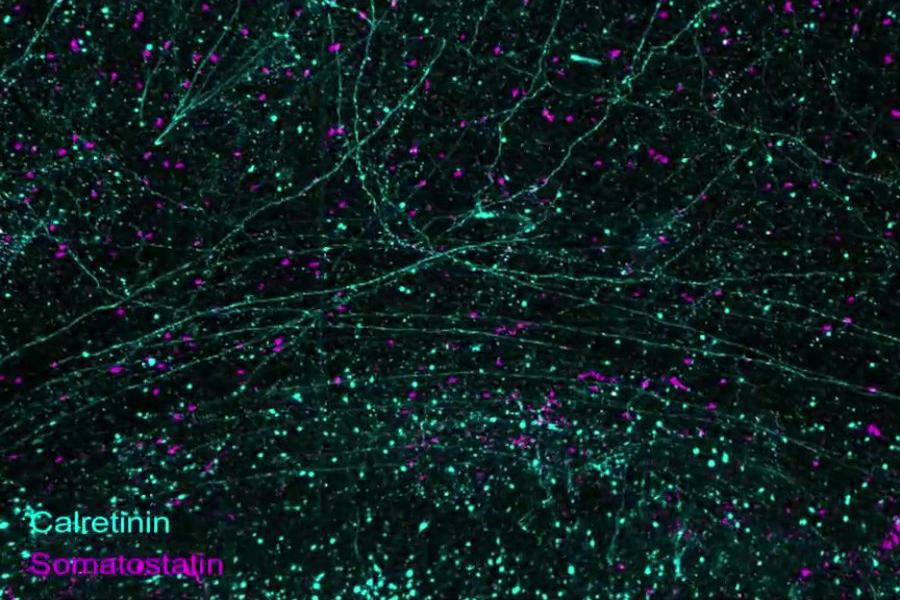
Observing anything and everything within the human brain, no matter how large or small, while it is fully intact has been an out-of-reach dream of neuroscience for decades. But in a new study in Science, an MIT-based team describes a technology pipeline that enabled them to finely process, richly label, and sharply image full hemispheres of the brains of two donors — one with Alzheimer’s disease and one without — at high resolution and speed.


